Page 66 - The Hong Kong Green Building Council (HKGBC) 香港綠色建築議會
P. 66
Researches Zero Carbon Building in Hong Kong
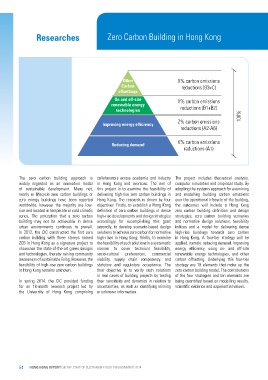
Other X% carbon emissions 100%
Carbon reductions (B3+C)
offsettings
On and off-site Y% carbon emissions
renewable energy reductions (B1+B2)
technologies
Z% carbon emissions
Improving energy efficiency reductions (A2-A6)
Reducing demand K% carbon emissions
reductions (A1)
The zero carbon building approach is collaborators across academia and industry The project includes theoretical analysis,
widely regarded as an innovative model in Hong Kong and overseas. The aim of computer simulation and empirical study. By
of sustainable development. Many net, this project is to examine the feasibility of adopting the systems approach for examining
nearly or lifecycle zero carbon buildings or delivering high-rise zero carbon buildings in and modelling building carbon emissions
zero energy buildings have been reported Hong Kong. The research is driven by four over the operational lifecycle of the building,
worldwide, however the majority are low- objectives. Firstly, to establish a Hong Kong the outcomes will include a Hong Kong
rise and located in temperate or cold climatic definition of zero carbon buildings in dense zero carbon building definition and design
zones. The perception that a zero carbon high-rise developments and design strategies strategies, zero carbon building scenarios
building may not be achievable in dense accordingly for accomplishing this goal; and normative design solutions, feasibility
urban environments continues to prevail. secondly, to develop scenario-based design indices and a model for delivering dense
In 2012, the CIC constructed the first zero solutions to achieve zero carbon for normative high-rise buildings towards zero carbon
carbon building with three storeys named high-rises in Hong Kong; thirdly, to examine in Hong Kong. A four-tier strategy will be
ZCB in Hong Kong as a signature project to the feasibility of such solutions in a systematic applied, namely: reducing demand, improving
showcase the state-of-the-art green designs manner to cover technical feasibility, energy efficiency, using on- and off-site
and technologies, thereby raising community socio-cultural preferences, commercial renewable energy technologies, and other
awareness of sustainable living. However, the viability, supply chain competency, and carbon offsetting. Underlying this four-tier
feasibility of high-rise zero carbon buildings statutory and regulatory acceptance. The strategy are 10 elements that make up the
in Hong Kong remains unknown. final objective is to verify such solutions zero carbon building model. The contributions
in real cases of building projects by testing of the four strategies and ten elements are
In spring 2014, the CIC provided funding their sensitivity and dynamics in relation to being quantified based on modelling results,
for an 18-month research project led by uncertainties, as well as identifying missing scientific evidence and experiential values.
the University of Hong Kong comprising or unknown information.
64 HONG KONG REPORT ON THE STATE OF SUSTAINABLE BUILT ENVIRONMENT 2014
Other X% carbon emissions 100%
Carbon reductions (B3+C)
offsettings
On and off-site Y% carbon emissions
renewable energy reductions (B1+B2)
technologies
Z% carbon emissions
Improving energy efficiency reductions (A2-A6)
Reducing demand K% carbon emissions
reductions (A1)
The zero carbon building approach is collaborators across academia and industry The project includes theoretical analysis,
widely regarded as an innovative model in Hong Kong and overseas. The aim of computer simulation and empirical study. By
of sustainable development. Many net, this project is to examine the feasibility of adopting the systems approach for examining
nearly or lifecycle zero carbon buildings or delivering high-rise zero carbon buildings in and modelling building carbon emissions
zero energy buildings have been reported Hong Kong. The research is driven by four over the operational lifecycle of the building,
worldwide, however the majority are low- objectives. Firstly, to establish a Hong Kong the outcomes will include a Hong Kong
rise and located in temperate or cold climatic definition of zero carbon buildings in dense zero carbon building definition and design
zones. The perception that a zero carbon high-rise developments and design strategies strategies, zero carbon building scenarios
building may not be achievable in dense accordingly for accomplishing this goal; and normative design solutions, feasibility
urban environments continues to prevail. secondly, to develop scenario-based design indices and a model for delivering dense
In 2012, the CIC constructed the first zero solutions to achieve zero carbon for normative high-rise buildings towards zero carbon
carbon building with three storeys named high-rises in Hong Kong; thirdly, to examine in Hong Kong. A four-tier strategy will be
ZCB in Hong Kong as a signature project to the feasibility of such solutions in a systematic applied, namely: reducing demand, improving
showcase the state-of-the-art green designs manner to cover technical feasibility, energy efficiency, using on- and off-site
and technologies, thereby raising community socio-cultural preferences, commercial renewable energy technologies, and other
awareness of sustainable living. However, the viability, supply chain competency, and carbon offsetting. Underlying this four-tier
feasibility of high-rise zero carbon buildings statutory and regulatory acceptance. The strategy are 10 elements that make up the
in Hong Kong remains unknown. final objective is to verify such solutions zero carbon building model. The contributions
in real cases of building projects by testing of the four strategies and ten elements are
In spring 2014, the CIC provided funding their sensitivity and dynamics in relation to being quantified based on modelling results,
for an 18-month research project led by uncertainties, as well as identifying missing scientific evidence and experiential values.
the University of Hong Kong comprising or unknown information.
64 HONG KONG REPORT ON THE STATE OF SUSTAINABLE BUILT ENVIRONMENT 2014