7
1. Introduction
1.1 HK3030 Campaign
Buildings take up over 90% of electricity
consumption in Hong Kong and account
for more than 60% of the greenhouse gases
(GHG) emitted citywide. Hence, building
sector has great potential in contributing to
the city’s GHG reduction target [1].
Hong Kong Green Building Council Limited
(HKGBC) was established in 2009 to lead
the market transformation to a sustainable
built environment. Over the last 5 years, the
council has played a major role in guiding
the transformation by developing industry
standards and best practices, as well as
delivering educational programmes and
initiating research in green buildings.
Recently, the HKGBC launched the HK3030
Campaign, an initiative to focus and
coordinate the demand-side management
approach to electricity consumption [2].
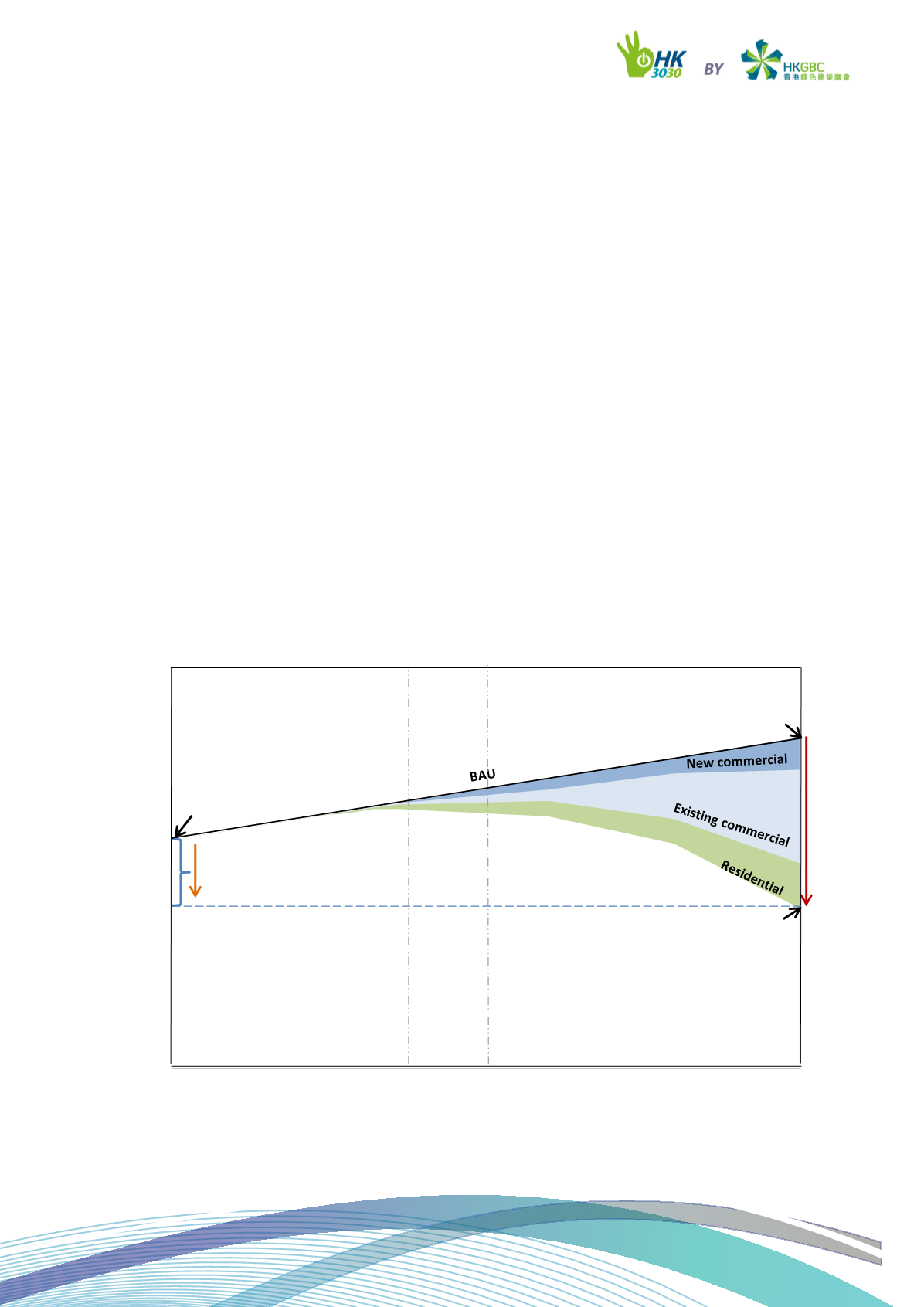
The objective of the campaign is to enable
a reduction of 30% to the absolute building
electricity consumption by 2030, as
compared to the level of 2005. Taking into
account the projected increase in building
stocks and higher energy consumption per
capita, HK3030 Campaign is equivalent to
a reduction of 52% in absolute electricity
consumption compared to a Business-As-
Usual (BAU) scenario.
0
10000
20000
30000
40000
50000
60000
2005
2006
2007
2008
2009
2010
2011
2012
2013
2014
2015
2016
2017
2018
2019
2020
2021
2022
2023
2024
2025
2026
2027
2028
2029
2030
In 2005:
34,548 GWh
HK
30
30
Target:
24,185 GWh
30%
10,364 GWh
52%
2030 BAU:
50,000 GWh
Building Electricity Consumption Prediction by 2030
Year
Building Electricity Consumption in Hong Kong (GWh)
0
50,
40,
30, 0
20,000
10,000
60,
2005
2014
2017
2030